AI Chatbot vs AI Agent: What's the difference?
An AI chatbot is designed for simple, often scripted, question-answer interactions, while an AI agent is more autonomous, goal-driven, and capable of taking actions, making decisions, or performing tasks on your behalf.
🤖 What is an AI Chatbot?
An AI chatbot is a conversational interface designed to simulate human-like interactions through text or voice. It utilizes artificial intelligence, particularly Natural Language Processing (NLP), to understand and respond to user inputs in natural language.
Here’s what defines an AI chatbot:
- Purpose-built for conversation. Its main role is to communicate clearly, answering questions and guiding users through information.
- NLP-driven understanding. It uses machine learning models to interpret a wide variety of user questions—even when phrased in different ways.
- Reactive interaction. It typically waits for the user to ask something and then responds. It doesn’t take initiative or perform tasks on its own.
- Predefined knowledge and flows. Many chatbots use carefully scripted or trained responses to ensure accuracy and brand safety.
- Limited memory or personalization. While some advanced chatbots can remember context within a session, most do not retain information over time or adapt deeply to individual users.
- Easy to deploy. Many SaaS platforms let you build and integrate chatbots quickly with low-code or no-code tools.
✅ Best suited for:
- Customer service FAQs
- Answering product questions
- Collecting contact details or qualifying leads
- Guiding users through website or app flows
- Reducing human support volume for simple requests
Bottom line: AI chatbots excel at responsive, human-like conversation to provide information or simple guidance quickly and at scale.
🧭 What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a more advanced, autonomous system that goes beyond conversation to achieve specific goals on behalf of the user. While an agent might talk, its defining strength is that it can act.
Here’s what sets AI agents apart:
- Agency and autonomy. Agents don’t just respond, they make decisions and take action to complete tasks, even with minimal human input.
- Goal-oriented design. An agent is given an objective (e.g., “book me a flight,” “find the cheapest supplier,” “resolve a refund”) and it figures out how to accomplish it.
- Chained reasoning and planning. Agents can break goals into steps, plan execution, and adapt if something changes.
- Tool and API integrations. Agents often interact with external systems, such as booking platforms, databases, CRMs, and payment processors, to get work done.
- Memory and context. Many agents maintain state over time, remember past interactions, or store user preferences to personalize results.
- Proactive behavior. Unlike purely reactive chatbots, agents can suggest next steps, initiate conversations, or follow up without being prompted.
✅ Best suited for:
- Automating complex, multi-step workflows
- Handling operational tasks that normally require human intervention
- Personal digital assistants that execute real commands
- Research and summarization across multiple sources
- Sales outreach that involves sequencing and follow-ups
Bottom line: AI agents aren’t just about conversation. They’re about doing real work. They can plan, decide, and act in a way that reduces manual effort and unlocks true automation.
Overview: How do Chatbots and Agents Differ?
| Feature | AI Chatbot | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Answer questions, guide conversations, qualify leads | Achieve goals, complete tasks autonomously |
| Initiative | Reactive—waits for user prompts | Proactive or reactive—can initiate actions |
| Complexity | Simple, predictable dialogues | Complex planning, decision-making, multi-step workflows |
| Interaction Style | Conversational only | Conversational plus actions and tool use |
| Memory & Context | Limited or session-based | Persistent memory, user personalization |
| Integration Level | Basic (FAQs, CRM handoffs) | Advanced (APIs, databases, external systems) |
| Tech Stack Needs | Low-code/no-code platforms; simple APIs | Frameworks for orchestration, memory, tool use |
| Cost to Build & Run | Generally cheaper and faster to deploy | More expensive; requires more resources and monitoring |
| User Experience | Predictable, controlled, brand-safe | Dynamic, can surprise users, requires onboarding |
| Best Suited For | Customer service FAQs, lead capture, simple support | Automating bookings, research, task completion |
| Example Use Cases | Website FAQ widgets, Messenger bots, in-app help | Travel booking assistants, sales outreach automation, refund processors |
| Bottom Line | Lightweight, user-guided conversations for quick answers | Real automation that plans, decides, and acts on your behalf |
When Should You Use Each?
Choosing between a chatbot and an AI agent isn’t just about technology. It’s about matching the right tool to the problem you want to solve.
Here’s how to decide:
🤖 Use a Chatbot When…
- Your main goal is communication. You want to answer questions, collect user input, or provide information in a natural conversational style.
- You have predictable, repeatable interactions. FAQs, store hours, order status, password resets → Anything you can script or prompt.
- You need fast time-to-value. Many chatbot platforms are no-code or low-code, with pre-built templates. You can deploy them quickly without heavy engineering.
- You want to qualify or route leads. A chatbot can ask screening questions, collect contact details, and hand off to human sales or support.
- You need controlled, brand-safe answers. Chatbots can be restricted to approved responses, minimizing risk of inappropriate or incorrect output.
- Example Use Cases:
- E-commerce FAQ widget
- Lead capture on landing pages
- In-app help for SaaS products
✅ Bottom line: Choose a chatbot when you want lightweight, predictable, user-guided conversations that improve support or sales efficiency without much complexity.
🧭 Use an AI Agent When…
- You want the system to act, not just talk. Agents don’t just answer → they execute tasks and interact with external tools or APIs.
- Your workflows involve multiple steps. Booking an appointment, processing a refund, sending follow-up emails, or generating a report.
- You need autonomous problem-solving. Agents can plan actions, handle contingencies, and adjust to changing inputs without constant human supervision.
- You want to save time on operational tasks. Agents can replace manual work, automate repetitive tasks, and integrate deeply with your existing systems.
- You’re ready to invest in more advanced capabilities. Agents often require custom integrations, testing, and monitoring to ensure reliability and safety.
- Example Use Cases:
- Automated travel booking assistant
- AI-powered sales outreach (prospect, email, follow up)
- Customer support agent that processes refunds or cancels subscriptions
✅ Bottom line: Choose an AI agent when you need real automation → something that can handle multi-step tasks, make decisions, and get things done on your behalf.
⚡ Pro Tip: You Don’t Have to Choose Just One
Many businesses start with chatbots to handle customer questions and then layer in agent-like capabilities for task execution. For example:
Your chatbot greets visitors and collects details → Your AI agent books an appointment or places an order.
This hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds: clear, user-friendly conversations plus real automation behind the scenes.
As an example, you can use Big Sur AI to have contextual, human-like conversations with visitors, while triggering automated actions in the background:
What are real-world examples of each?
AI Chatbots are everywhere: website support popups, in-app FAQs, and simple sales assistants that answer product questions.
Think Intercom, Drift, or even airline websites where you ask about flight times.
AI Agents go further.
Examples include sales prospecting bots that autonomously email leads and follow up, customer support agents that resolve tickets by triggering refunds, or personal assistants that schedule meetings for you by negotiating with calendars and email.
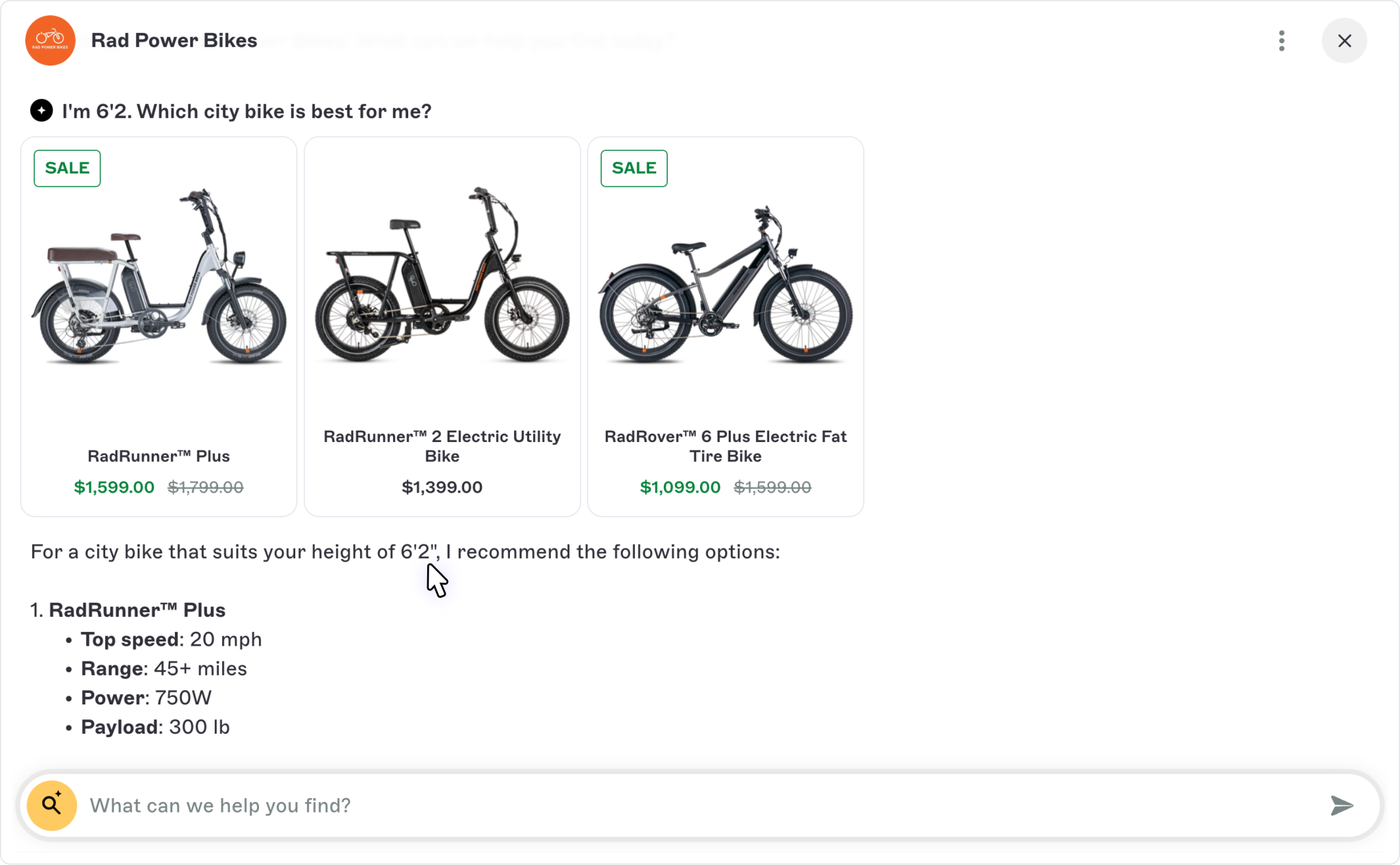
Agents don’t just answer, they act.
How do they work under the hood?
Chatbots typically use predefined rules, decision trees, or large language models (LLMs) to generate conversational responses. They’re good at dialogue, but need guidance to stay on topic.
AI Agents add planning and tool use. They set goals, break them into steps, use APIs or software tools, and adapt based on results. Under the hood, they combine LLMs with reasoning frameworks (like chains or trees of thought) to decide what to do next → not just what to say.
Do they require different tech stacks or tools?
Often, yes. Chatbots can run on simple platforms with UI-based flows or integrate with LLM APIs. Popular choices include Intercom, ManyChat, or custom bots with GPT.
Agents usually require orchestration frameworks, memory systems, and tool integrations. You’ll see agentic frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, or AI platform features that support multi-step plans and API calls. Building agents often needs more development time and engineering resources.
Are AI agents more expensive to build or run?
Generally, yes, agents cost more.
They require more advanced models (often with memory), integrations with tools or APIs, and robust monitoring to handle autonomy. Running costs can include more compute, storage for context or memory, and API call fees.
Chatbots can be cheaper, especially if you use pre-built SaaS solutions with simple per-user pricing. But for both, complexity drives cost: a very smart chatbot can also get expensive.
How does user experience differ?
With chatbots, users expect quick, direct answers.
They guide the conversation and usually stay in control. The UX is predictable.
Agents introduce autonomy: they might act for the user or surprise them by taking initiative. This can be powerful (they get things done) but requires careful design to avoid confusion or loss of trust.
Users might need onboarding or ways to approve/stop actions.
Can a chatbot become an agent?
Short answer: Yes!
Long answer: Many companies start with chatbots and evolve them into agents. Adding memory, tool use (like API calls), and planning turns a reactive Q&A bot into a proactive problem-solver.
It’s often a good strategy to launch simple, validate user needs, then add autonomy carefully. You don’t need to choose one forever, you can build in stages.
What are the risks or downsides of each?
Chatbots: they’re often too simple.
Users can get frustrated if they can’t handle nuance or context. They can hallucinate or go off-topic if LLM-based.
Agents: they’re more powerful but risk loss of control.
Autonomy can lead to unexpected actions, security issues (if they access systems), or user distrust if they’re not transparent. They also require more monitoring and testing.
How do you choose the right one for your business?
Ask yourself:
- What’s the problem you’re solving? Quick answers → chatbot. Completing tasks → agent.
- How much control do users need? Predictable flows → chatbot. Autonomy → agent.
- What’s your budget and timeline? Simpler chatbots are faster and cheaper to deploy.
- Do you have technical resources? Agents need more integration and testing.
A good rule: start small, then grow.
What’s the future of chatbots and agents?
Short answer: no one knows (although LinkedIn influencers will say otherwise).
The lines are blurring. Expect chatbots to become smarter with memory and context, while agents will get easier to deploy with no-code tools. Many companies will offer hybrid solutions that can answer questions and take action.
Overall trend: more autonomy, more personalization, and tighter integration with business systems.
How do they fit together? Do they even?
They’re not enemies → they’re complementary.
A chatbot can be the conversational front-end that understands user intent, while an agent does the work in the background.
For example, your chatbot asks for user details and passes them to an agent that books appointments, triggers refunds, or emails leads. The best systems combine both for seamless user experiences.
Need an AI agent that hand-holds website visitors?
Big Sur AI is a pre-built AI agent that can answer both simple and complex questions your website visitors might have, and take action to help drive conversions.
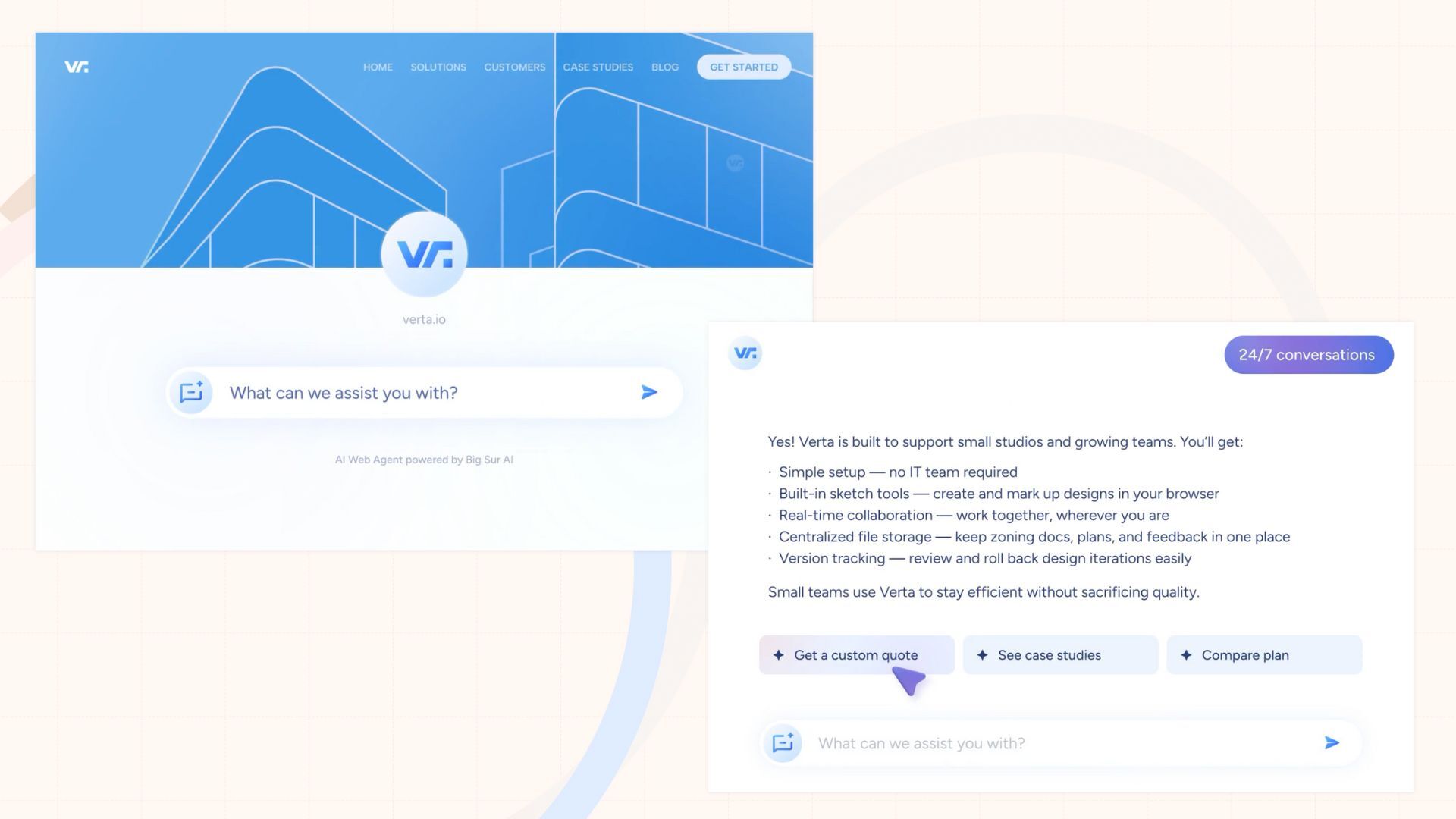
All you need to do is type in your URL, and your AI agent can be live in under 5 minutes ⤵️
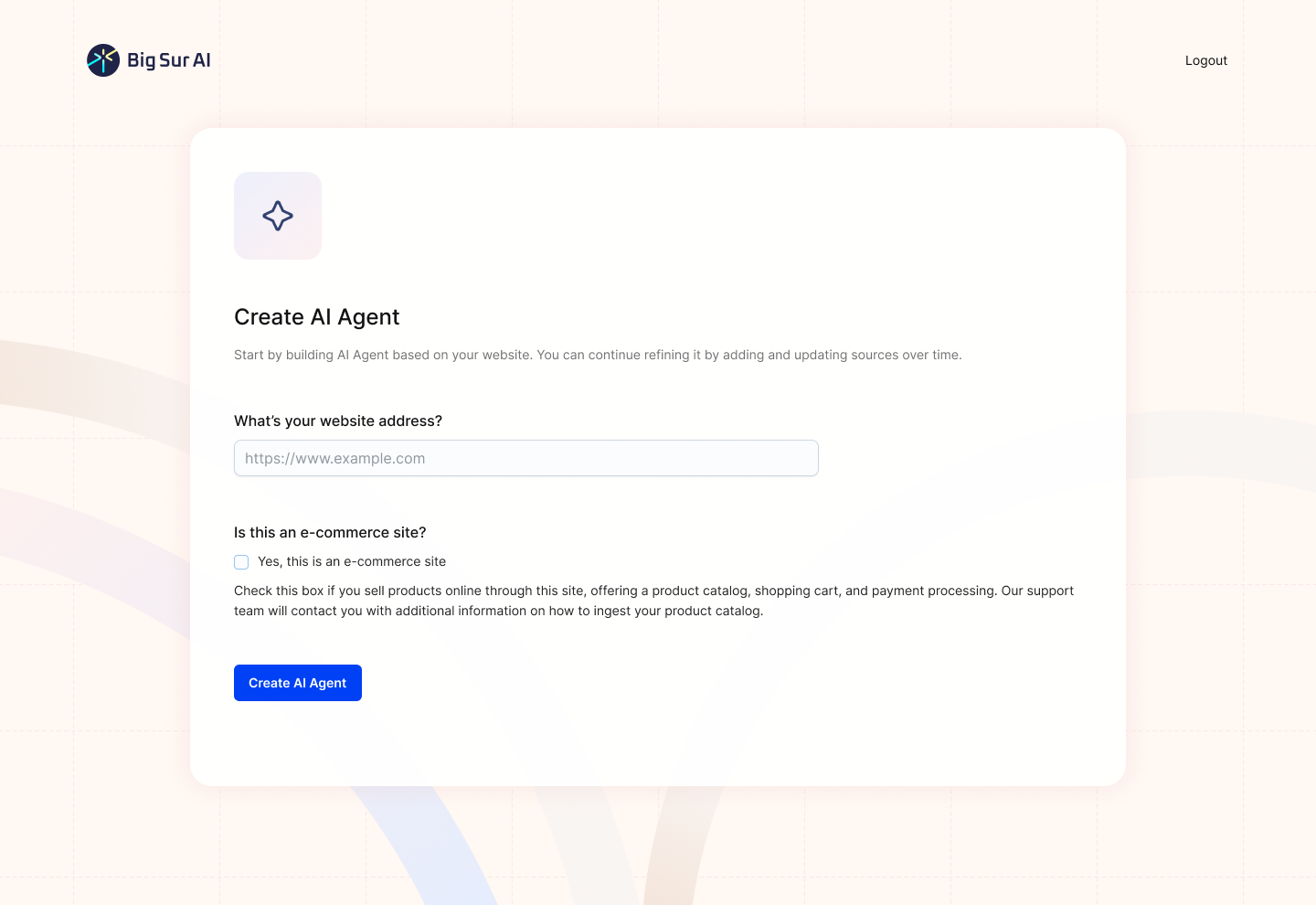
Here’s what you have to do:
- Sign up on Big Sur AI's Hub (link here).
- Enter your website URL. Big Sur AI will automatically analyze your site content.
- Customize your AI agent. Set up specific AI actions and decide where the AI agent will appear on your site.
- Launch and monitor. Your AI agent will be live in minutes, and you can track performance with real-time analytics.
Try Big Sur AI on your site in minutes by clicking the image below 👇