n8n vs Make: What's the best AI agent builder? [2025]
n8n vs Make is a common comparison because both offer powerful workflow automation, but users must choose between developer-grade flexibility and self-hosting (n8n) vs polished, no-code ease-of-use with 1,500+ integrations (Make).
This guide is designed to help you quickly get a sense of which tool is best for your needs.
Here’s what’s covered: Should you consider Big Sur AI instead, n8n vs Make overview, feature-by-feature breakdown, cost comparison, integrations and workflow building, AI capabilities, customization, customer reviews, pros and cons, and which is best for your business.
Let’s dive in 👇
Should you consider Big Sur AI instead?
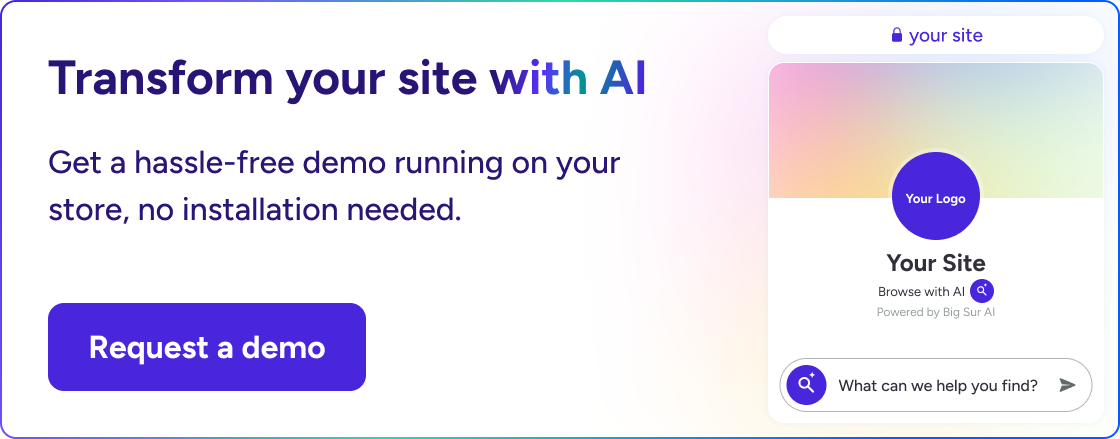
Reason 1: Zero setup, instant time-to-value
Big Sur AI launches a fully functional AI chatbot in minutes, skipping the need to design workflows, add modules, or debug integrations.
For sales lead capture, FAQ support, or customer onboarding, you can go live immediately without needing any code or workflow knowledge.
--> Try it here
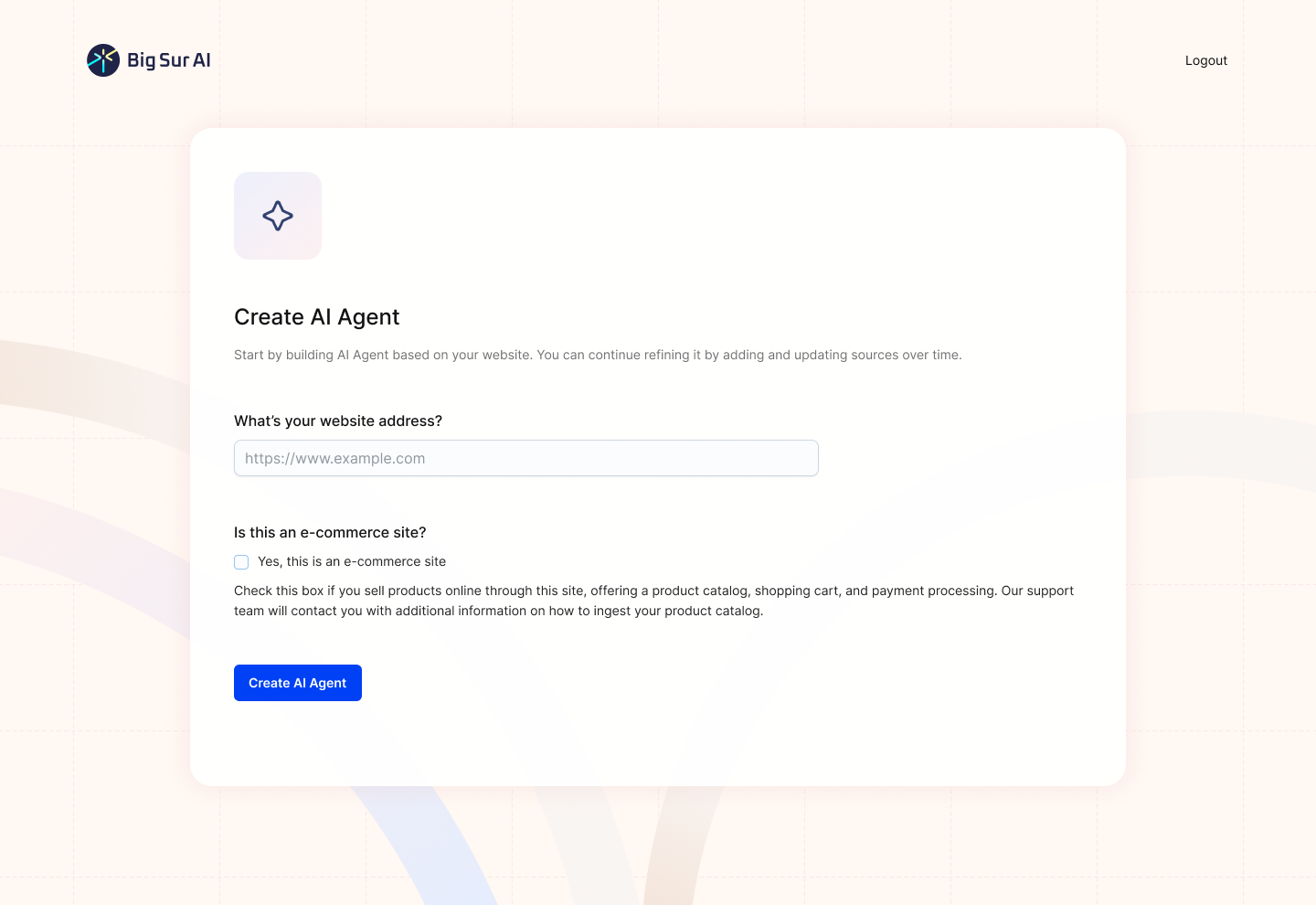
Reason 2: No tech headaches or developer dependencies
Big Sur AI eliminates API wrangling, webhook setup, and third-party integration work. Teams with no IT resources can simply add Big Sur AI to their site and start solving user questions instantly, without risking future technical debt.
The chatbot will automatically scan your documentation and website data to deliver highly accurate responses to complex questions.
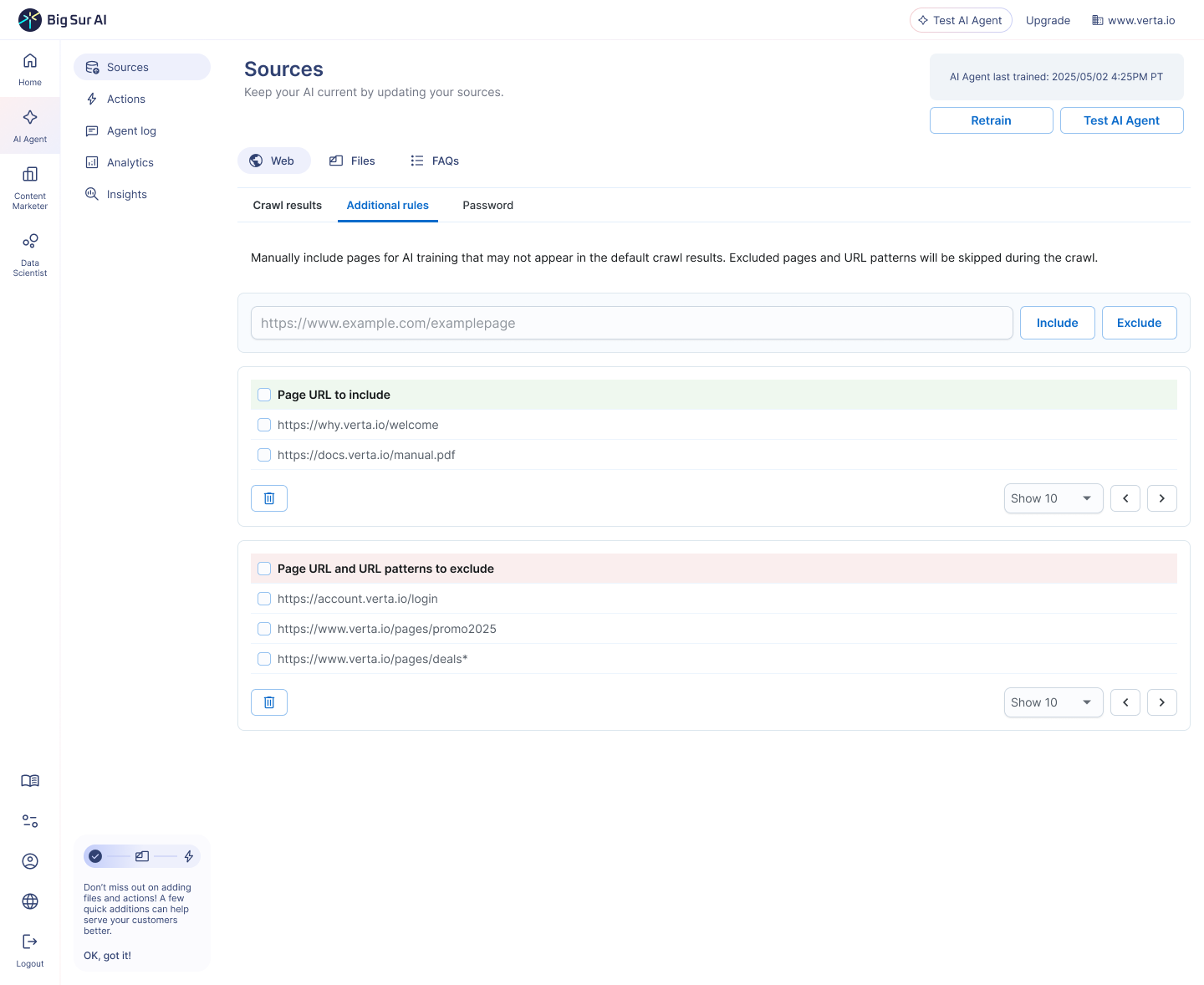
Reason 3: Purpose-built for conversational experiences
Big Sur AI comes optimized for the highest-demand AI use cases, including 24/7 customer support, knowledge base search, and proactive lead engagement on your website. Instead of piecing together logic nodes and branching tools, the agent’s behavior is ready out of the box.
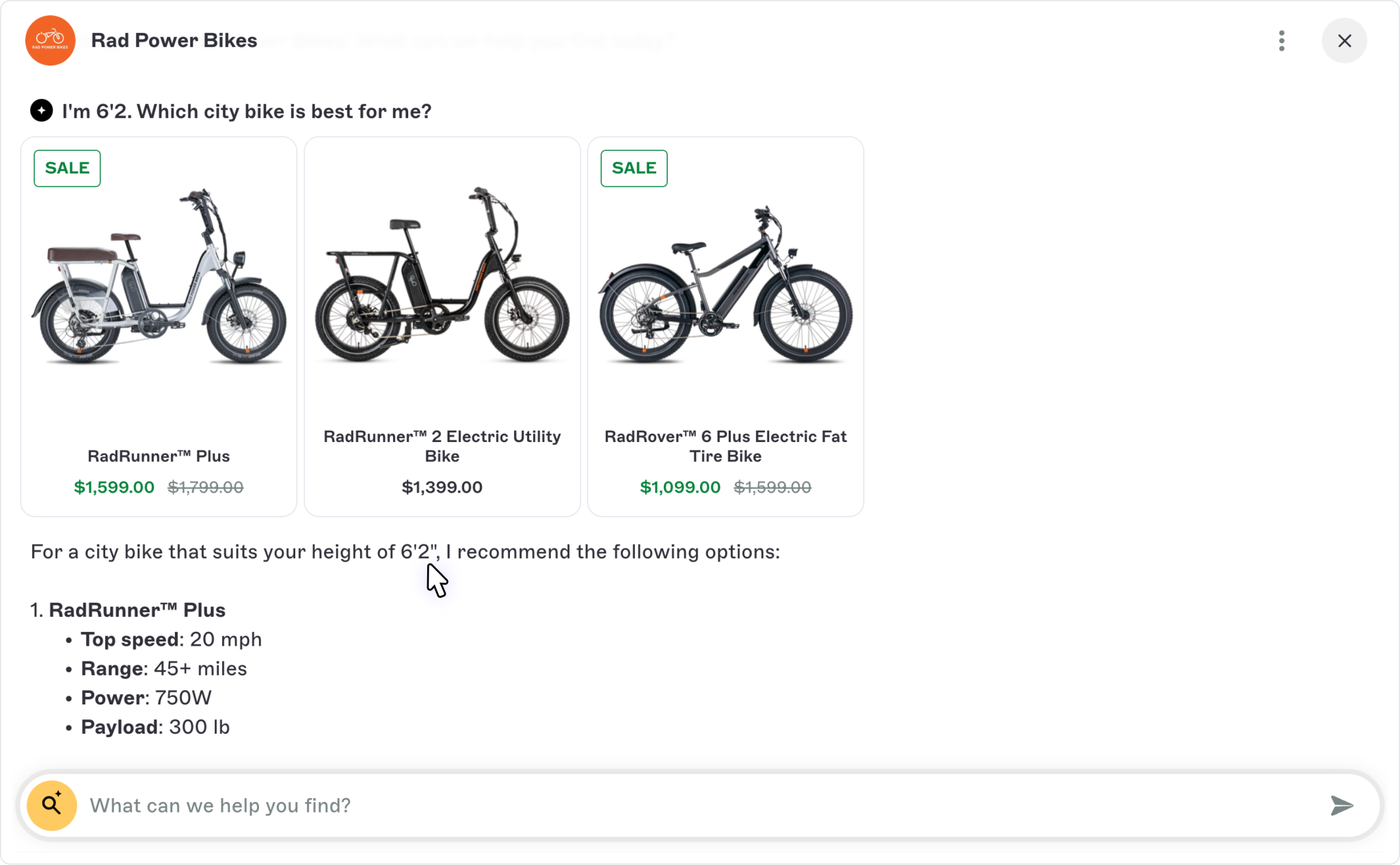
Reason 4: Custom-trained chatbot with agentic workflows
Big Sur AI trains on your own website pages and documentation data. Anything you can feed it.
The result is an AI chatbot that can give super precise and accurate responses to complex questions.

The chatbot can also fire agentic workflows when conversations match certain contextual criteria.
n8n vs Make: Overview
| Factor | n8n | Make (Integromat) |
|---|---|---|
| Public reviews | 4.7 ⭐ (G2), 4.8 ⭐ (Capterra) | 4.8 ⭐ (G2), 4.7 ⭐ (Capterra) |
| Our rating | 8.7/10 ⭐ | 9/10 ⭐ |
| Core purpose | Open-source workflow automation for technical users, developers, and teams needing full control | No-code/low-code workflow automation for businesses seeking fast, polished automation across SaaS apps |
| Best for | Technical users or teams, developers, companies requiring on-premise or custom automation | No-code makers, business teams, agencies, users needing a vast range of plug-and-play integrations |
| Typical use cases | Custom business workflows, internal automations, data routing, API orchestration, self-hosted integration | Business process automation, SaaS integration, marketing & sales automation, eCommerce ops, data sync |
| Hosted vs self-hosted? | Both: Fully self-hosted (open-source) or hosted cloud version | Hosted only (cloud-based SaaS) |
| Open Source? | ✅ Yes (Apache 2.0 license) | ❌ No |
| Pricing model | Free (self-hosted) + Pro/Business paid cloud subscriptions | Usage-based, tiered plans (operations/month and features) |
| Free plan? | ✅ Yes: unlimited workflows, self-hosted (community edition) | ✅ Yes (1,000 monthly ops, limited features) |
| Customization level | Very high (custom code, modules, node creation, webhooks, script support) | Medium (built-in modules, some custom code, but vendor-locked UI) |
| Ease of use | Moderate/advanced (some learning curve, ideal for technical users) | Very easy (drag-and-drop, visual builder, suitable for beginners) |
| LLM integrations | Yes (OpenAI, Cohere, GPT-4, Hugging Face, and custom LLM via HTTP nodes or community modules) | Yes (OpenAI, Google PaLM, Hugging Face, plus AI modules for text/image, but fewer open-ended options than n8n) |
| Other integrations | 450+ built-in, plus limitless via HTTP/REST APIs and community nodes | 1,500+ native app integrations (as of 2024), plus generic HTTP, webhook support |
| Workflow capabilities | Highly customizable, conditional branching, loops, variables, code nodes, error handling | Visual modular logic, branching, iterators, error handling, scheduling, but with more guardrails |
| Deployment options | Self-hosted (Docker, bare metal, cloud, Kubernetes) or n8n cloud | SaaS cloud only |
| Team collaboration | Team features (paid), workspace sharing, access controls, versioning in paid cloud | Team folders, scenario sharing, user roles, but only in higher paid tiers |
| Pros | ✅ Open source ✅ Total data/privacy control ✅ Unlimited workflows self-hosted ✅ Code & advanced logic |
✅ Huge app catalog ✅ Slick, no-code builder ✅ Strong documentation ✅ Fast to production for non-coders |
| Cons | ❌ Steeper learning curve ❌ Requires DevOps for self-host ❌ Fewer native integrations than Make |
❌ No self-hosting ❌ Usage-based pricing can escalate ❌ Vendor lock-in on advanced features |
| Why choose it? | 👉 Best for developers or teams needing open source, self-hosting, and maximal control/flexibility at scale | 👉 Best for business users who want rapid, low-code SaaS automations and vast plug-and-play integrations |
n8n vs Make: How do their features compare?
n8n wins on developer-grade flexibility and customization
n8n stands apart for users who need to go beyond drag-and-drop automations.
Unlike Make, n8n gives technical teams direct access to custom JavaScript in every node.
This means you can insert logic, transform data, and connect APIs that don’t have an official integration.
For example, creating a custom Slack notification that parses data from a legacy CRM—no prebuilt module required.
n8n’s open node structure appeals specifically to businesses that need to support niche use cases or who want to tweak automation behavior at a granular level.
Aka --> You’re not gated by what’s on a marketplace.
Make is better for out-of-the-box integrations
Make’s catalog of 1,500+ native integrations wins for businesses that want rapid deployment without any code.
You can connect Shopify, HubSpot, Airtable, or even apps like Monday.com with just a few clicks.
No need to create custom connectors or write scripts.
This lets users quickly automate sales, marketing, or operations workflows across a wider range of platforms.
As an example, a marketing team could drag-and-drop a sequence that moves data from Google Forms to Mailchimp, Slack, and a project tracker like Asana, all using 100% native steps.
This ease of automation is what no-code teams love.
Make is more favored by customers for visual workflow building
Make’s visual editor is consistently rated as more intuitive for non-developers.
Everything is organized on a real-time canvas, and it’s easy to see the flow of data between steps.
This makes Make more approachable for marketers, ops teams, and business users who want to automate processes without understanding scripting.
You can switch between flowchart mode and low-level configuration seamlessly.
Practically speaking, a new user can go from zero to a working workflow in minutes.
With n8n, the editor is less beginner-friendly, especially as workflows get more complex.
n8n has an edge with integration extensibility
If you need to work with an app or API not supported natively, n8n’s flexibility outpaces Make.
n8n lets you create custom nodes, use HTTP request nodes with authentication, or publish your own integrations to the n8n community hub.
For example, if your warehouse uses a proprietary REST API, you can build an n8n node for it and reuse it in multiple automations.
With Make, unsupported services require workarounds or aren’t possible without waiting for official support.
This means n8n is ideal when business-critical systems fall outside the mainstream SaaS ecosystem.
Make wins for pricing predictability and fair usage
Make’s pricing tiers are built on scenario executions and data operations, which makes cost forecasting straightforward.
There’s also a free tier generous enough for many SMB use cases.
In comparison, n8n’s pricing (for their cloud version) is based on workflow executions and often involves self-hosted maintenance overhead for the open-source tier.
For fast-growing teams that don’t want to worry about server costs, upgrades, or unpredictable limits, Make’s billing structure is simpler and less likely to hit surprise roadblocks as you scale.
This predictability is why many teams with rapidly expanding automations favor Make for high-volume scenarios.
n8n vs Make: How much do they cost?
n8n's pricing: quick overview
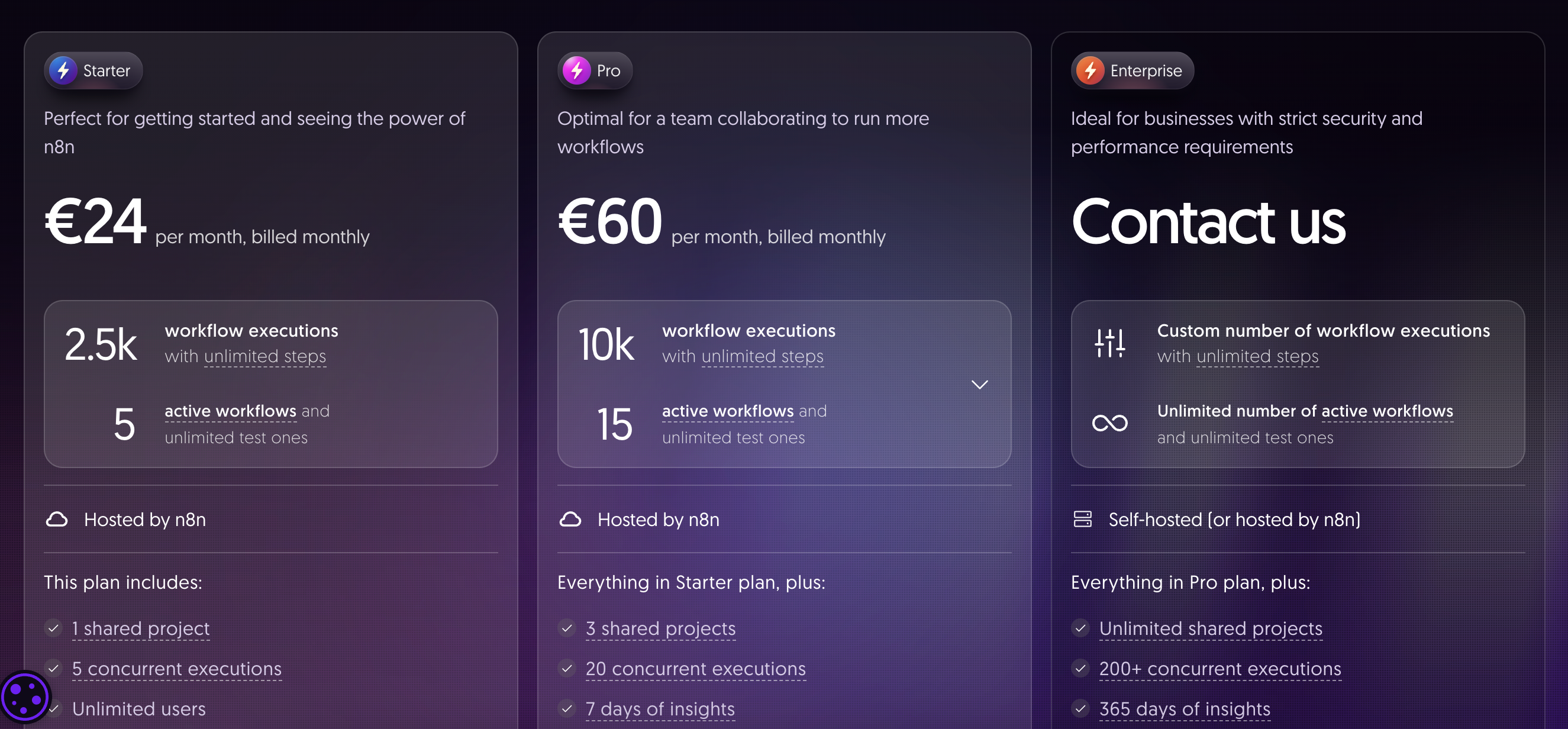
- Offers both cloud-hosted and self-hosted options
- Pricing is based primarily on the number of workflow executions per month and whether you need cloud hosting
- Updated pricing (as of June 2024):
- Free: Up to 200 workflow executions/month (cloud) or unlimited (self-hosted, open source)
- Pro (Cloud): Starts at $20/user/month with 10,000 executions included; ~$15 for each additional 10,000 executions
- Business (Cloud): Starts at $120/month for teams, with SSO and higher quotas
- Enterprise (Cloud or Self-hosted): Custom pricing available
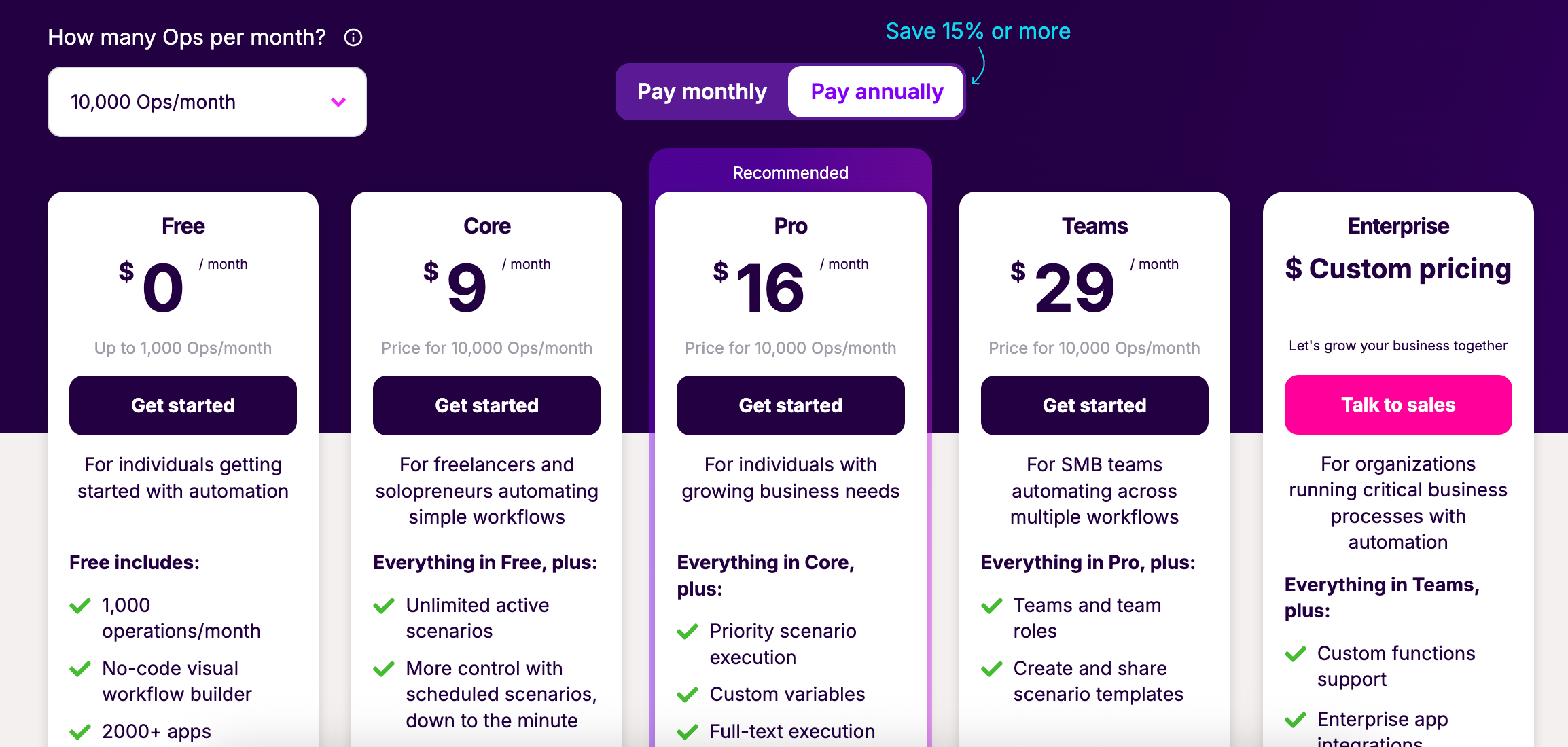
Make's pricing: quick overview
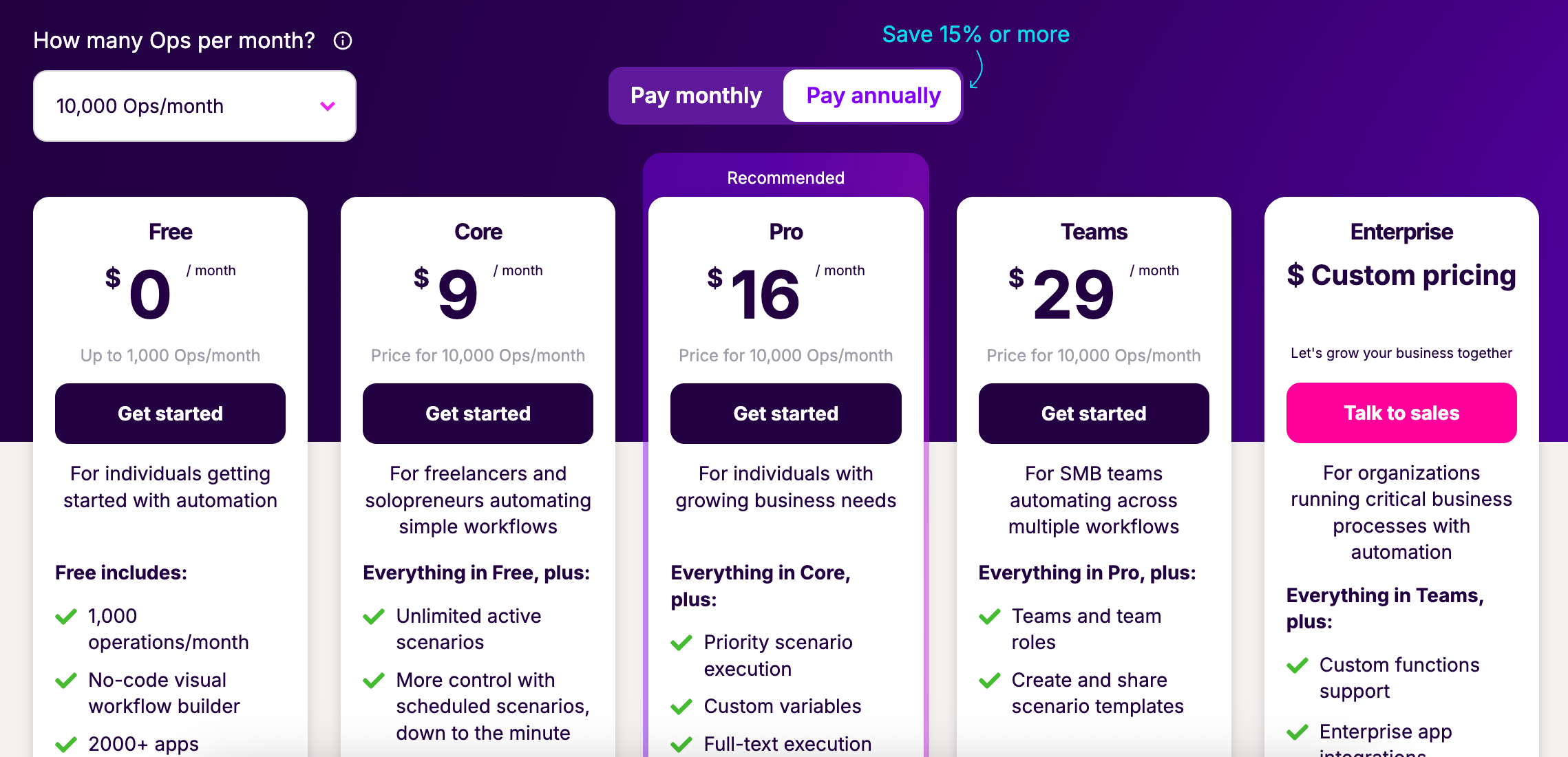
- Pricing is usage-based, counting "operations" (actions/steps inside a scenario)
- Cloud-only platform, no self-hosted option
- Updated pricing (as of June 2024):
- Free: 1,000 operations/month, 100MB data transfer, 2 active scenarios
- Core: $10.59/month, 10,000 operations, 1GB data transfer, unlimited scenarios
- Pro: $18.82/month, 40,000 operations, 20GB transfer, advanced features, premium support
- Teams & Enterprise: Scaling plans with increased limits, SSO, priority support
Key differences between each pricing structure
- n8n charges based on workflow executions, while Make charges per operation (each individual action in a workflow is counted)
- n8n is open-source and can be completely free if self-hosted; Make does not offer a self-hosted deployment
- Make is more granular—heavy multi-step scenarios may count as dozens of operations even within a single execution
How generous are each free plans?
- n8n Free:
- 200 executions/month on cloud
- Unlimited executions with self-hosted, open-source version (but you manage hosting and scaling)
- Core features, basic support
- Make Free:
- 1,000 operations/month (could be 100s of simple scenarios, or a handful of complex ones)
- 2 active scenarios
- 15-minute minimum scheduling interval
- Community support only
How does pricing increase with heavy usage?
- n8n:
- Cloud: +$15 per 10,000 extra executions
- Self-hosted: No usage-based charges, but you pay your own infra costs
- Additional charges for user seats or team features
- Make:
- Price increases as you need more operations or higher data transfer
- Adding more scenarios or teammates bumps you up to higher tiers
- Large businesses with complex scenarios can face steep scaling costs
Other potential surprises
- n8n:
- Executions are counted at the workflow level—a complex workflow or error handling doesn't multiply cost as rapidly
- Self-hosted flexibility means "free" has real infrastructure and maintenance expenses
- Make:
- Each step (even simple ones) counts as an operation, so costs can ramp quickly for long scenarios
- Premium app connectors are gated at higher tiers
- Data transfer limits could affect heavy file or API users
n8n vs Make: Integrations & Workflows
Integration breadth and depth
n8n supports over 350 native integrations and offers flexible connection via API, webhooks, and custom code nodes. Developers can extend its functionality to nearly any service, especially self-hosted or niche platforms. Built-in triggers support event-based automation.
Make features a much wider library with 1,500+ ready-to-use app integrations, covering popular SaaS products, enterprise tools, and industry APIs. Its marketplace provides additional community-built modules for rapid expansion.
Workflow building and complexity
n8n enables visual workflow creation with powerful conditional logic, loops, branching, and sub-workflows. It caters especially to users with technical backgrounds who need granular control or complex automation. Workflows are version-controlled and reusable.
Make offers a drag-and-drop editor focused on ease of use, enabling fast automation building without coding. Visual scenarios support conditional paths, error handling, scheduling, and multi-step flows. While less code-centric, Make streamlines automation for all skill levels.
Hosting and deployment
n8n can be self-hosted for maximum control, with options for on-premises deployment and cloud hosting. This is ideal for businesses with strict data policies or custom integration needs.
Make is fully cloud-based, requiring no infrastructure management. This reduces setup time and maintenance, but offers less control over data residency and customization.
n8n vs Make: AI capabilities
When evaluating n8n and Make for AI-driven workflow automation, consider the following tactical differences:
- Integration approach
- n8n: Supports AI via flexible HTTP Request nodes, OpenAI, Hugging Face, Google AI, and custom scripts. Users can connect any AI or LLM service, use custom prompts, and chain complex data transformations.

- Make: Offers visual, no-code modules for OpenAI, Google AI, Microsoft Azure AI, and built-in AI tools like image recognition and text analysis. Custom HTTP calls are supported but require less scripting.
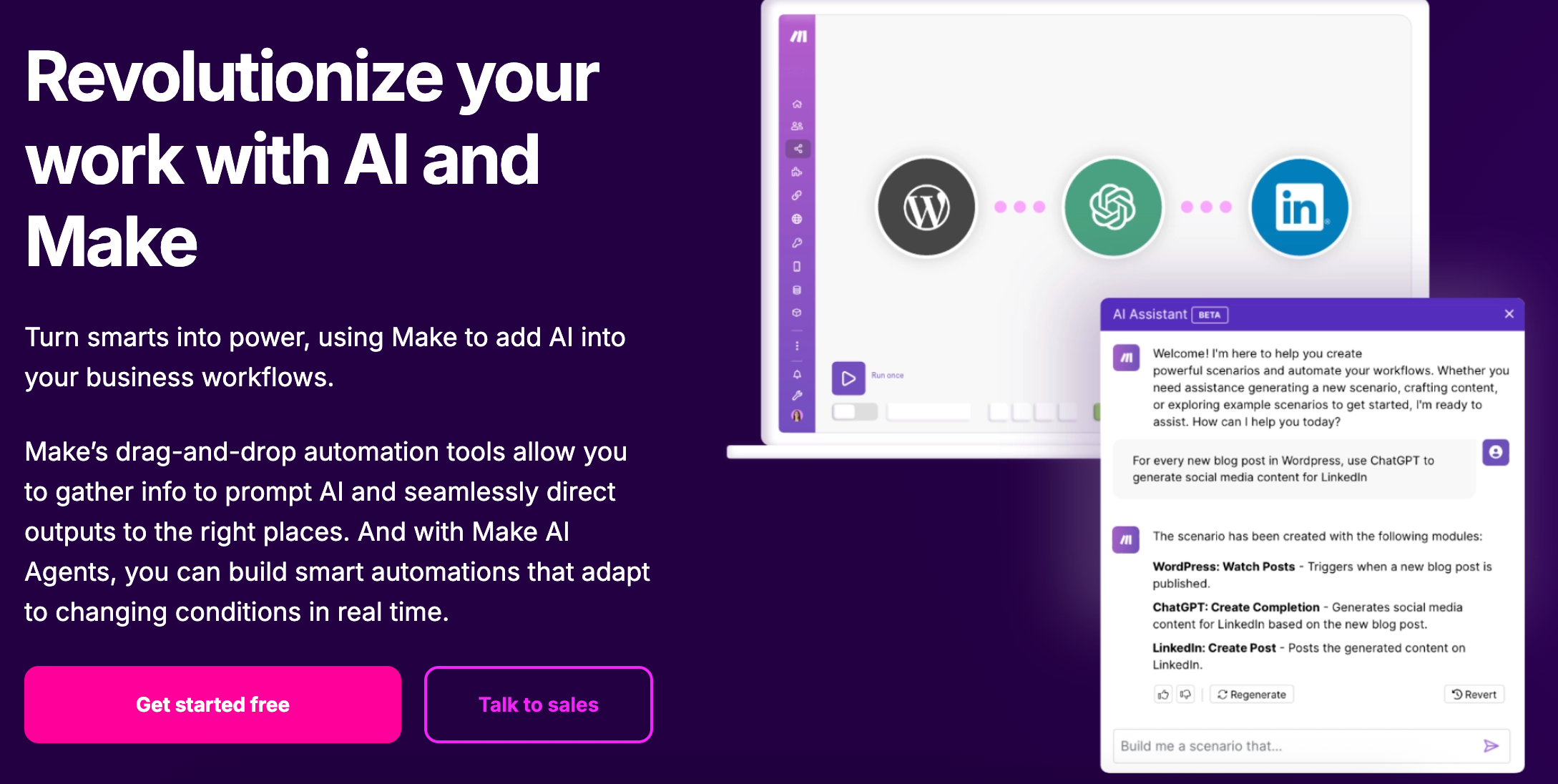
- Advanced AI workflow potential
- n8n: Allows advanced chaining, error handling, variable routing, and custom data parsing, making it ideal for users who want to build bespoke AI agents and complex decision trees.
- Make: Streamlines access to pre-built AI blocks, focusing on ease-of-use and speed for mainstream use cases like summarization, translation, sentiment, transcription, and image analysis.
- Extensibility
- n8n: Open source and self-hosted, enabling integration with private AI models, on-premise inference servers, and fine-tuned LLMs. High extensibility if your business requires internal data privacy or regulated workflows.
- Make: Primarily reliant on vendor-supported modules. User-created modules exist but custom logic is usually limited compared to n8n.
- Best use case fit
- n8n: Recommended for technical teams and businesses needing tight control over AI workflows, ability to mix and match model providers, and robust data transformation before/after AI calls.
- Make: Ideal for marketing, support, or ops teams seeking fast AI workflow assembly without deep AI or coding knowledge.
| Tool | AI integrations | Custom AI support | Best for | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n8n | OpenAI, Hugging Face, Google AI, any REST API | Strong (custom prompts, self-hosted models, custom logic via scripting) | Technical teams, advanced workflows, data privacy | Steeper learning curve, requires setup |
| Make | OpenAI, Google AI, Azure AI, pre-built AI modules | Moderate (HTTP modules, limited scripting, mostly no-code) | No-code users, fast setup of standard AI tasks | Less control, customization limited to integrated modules |
n8n vs Make: How customizable are they?
n8n offers deep developer control
n8n is designed for users who want maximum control over their workflows.
It’s open-source and self-hostable, so you can run it anywhere and even modify its core code. You can write custom JavaScript code at any step, build your own nodes, and connect to any API, including private or legacy endpoints.
This makes n8n highly flexible for unique AI agent use cases that need more than basic integrations or that require handling sensitive data in-house.
Make focuses on no-code convenience
Make (formerly Integromat) makes customization easy without any coding skills. Its visual builder lets you drag and drop modules from over 1,500 pre-built integrations, making it beginner-friendly.
You can set conditions, map data, and create scenarios using the visual flow, but advanced customization is limited to what’s available out-of-the-box.
Make does offer some scripting with built-in functions, but less flexibility compared to n8n for highly custom logic or external API connections.
n8n vs Make reviews: What do customers say?
TL;DR: Both n8n and Make score highly among customers, but for different reasons. n8n is praised for flexibility, openness, and self-hosting, while Make is chosen for ease-of-use, no-code building, and a wide array of integrations. The trade-off is control vs simplicity.
Here are their respective scores on major review sites ⤵️
n8n’s G2 score: 4.7/5 ⭐
n8n’s Capterra score: 4.8/5 ⭐
Make’s G2 score: 4.8/5 ⭐
Make’s Capterra score: 4.8/5 ⭐
Here’s what users say about both platforms 👇
n8n: The good
Reviews consistently highlight the “powerful customization options” and “control over automations” that n8n provides:
“n8n lets me self-host and add custom logic, which is a game-changer for privacy and advanced workflows.”
Open-source status is another draw. Developers note on Reddit and G2 that n8n doesn’t lock them in:
“You’re not tied to a SaaS. If you need to add a node, just code it up.”
Other positives in customer comments:
- Active community and documentation
- Cheaper at scale due to self-hosting
- Works well for complex or highly-specific business logic
n8n: The bad
Negative reviews focus on a learning curve and tools that feel “developer-first”:
“Setting up took me longer than with Zapier or Make, even after following the docs.”
Common complaints include:
- UI/UX feels rough compared to Make
- Lacks the breadth of “ready-to-go” pre-built integrations
- Occasional stability hiccups after updates
- Not best for teams without technical skills
Make: The good
Ease-of-use dominates positive reviews:
“Make’s visual editor is a huge advantage. I can create automations in minutes, no coding needed.”
Users highlight over 1,500+ integrations and high approachability for teams with little technical experience:
“I tried n8n before, but Make just made sense out of the box and got my team running faster.”
Additional feedback includes:
- Extremely intuitive drag-and-drop interface
- Excellent for rapid prototyping and scaling automations
- Pre-built templates for common use-cases
Make: The bad
Negative reviews tend to discuss platform limitations, pricing, and lock-in:
“Sometimes you hit a feature wall unless you’re on the most expensive plan.”
Other issues raised include:
- Runs in the cloud only, no self-hosting
- Expensive for high-volume operations
- Debugging and custom scripting is limited for advanced users
- Service disruptions or downtime affect everyone (since it’s fully SaaS)
The bottom line: n8n gets developer teams excited for self-hosted, flexible automation. Make is favored by businesses looking for speed, simplicity, and robust plug-and-play reliability at the cost of ultimate customization.
n8n vs Make: Pros and Cons for each
TL;DR:
🛠️ n8n is ideal for users who need advanced customization, developer-grade control, or self-hosting, and don’t mind a steeper learning curve to gain maximum flexibility.
🎨 Make (formerly Integromat) is best for teams wanting a plug-and-play, no-code experience, with a highly polished interface and out-of-the-box integrations, but less freedom for complex custom automations or on-premise deployments.
| Tool | Best For | Key Strength | Drawbacks | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n8n | Developers, technical teams, companies needing self-hosting or custom workflows | Open source, self-hostable, high flexibility, custom scripting, great for advanced/complex automations | Steeper learning curve, fewer pre-built integrations, interface less polished, initial config required | Free (self-hosted); Cloud from $20/mo |
| Make | No-code users, teams that want quick setup and a large integration library | Extremely user-friendly, 1,500+ integrations, visual editor, quick to deploy, robust templates | No self-hosting, less customization for complex logic, advanced features often paywalled | Free tier; Paid plans from $10.59/mo |
The bottom line: Which tool is better for my business?
- Choose n8n if you want maximum control, developer-grade customization, or must self-host for data privacy and compliance. n8n is open source, highly extensible, best for complex and proprietary automations, advanced AI chaining, and businesses with technical teams. It is also the most cost-effective option at scale if you can manage your own infrastructure.
- Choose Make if you value rapid, no-code workflow building, a polished visual interface, and need access to 1,500+ prebuilt integrations out of the box. Make is ideal for non-technical users and business teams who want to automate common SaaS apps quickly, track costs easily, and avoid handling any infrastructure or server maintenance.
- If you need deep AI customizations or wish to connect with niche tools or private/local AI models, n8n is the more flexible fit. For standard AI automations and broad integration needs that just work fast, Make will get you results with minimal setup or coding.
- Pick based on your team’s technical skills and priorities: n8n gives you control and extensibility for power users; Make wins for plug-and-play simplicity at scale.
Ready for even faster AI deployment?
Give Big Sur AI a try for instant, zero-setup conversational AI at https://hub.bigsur.ai/login.