What Are AI Agents? How They Work & How to Use Them in 2025?
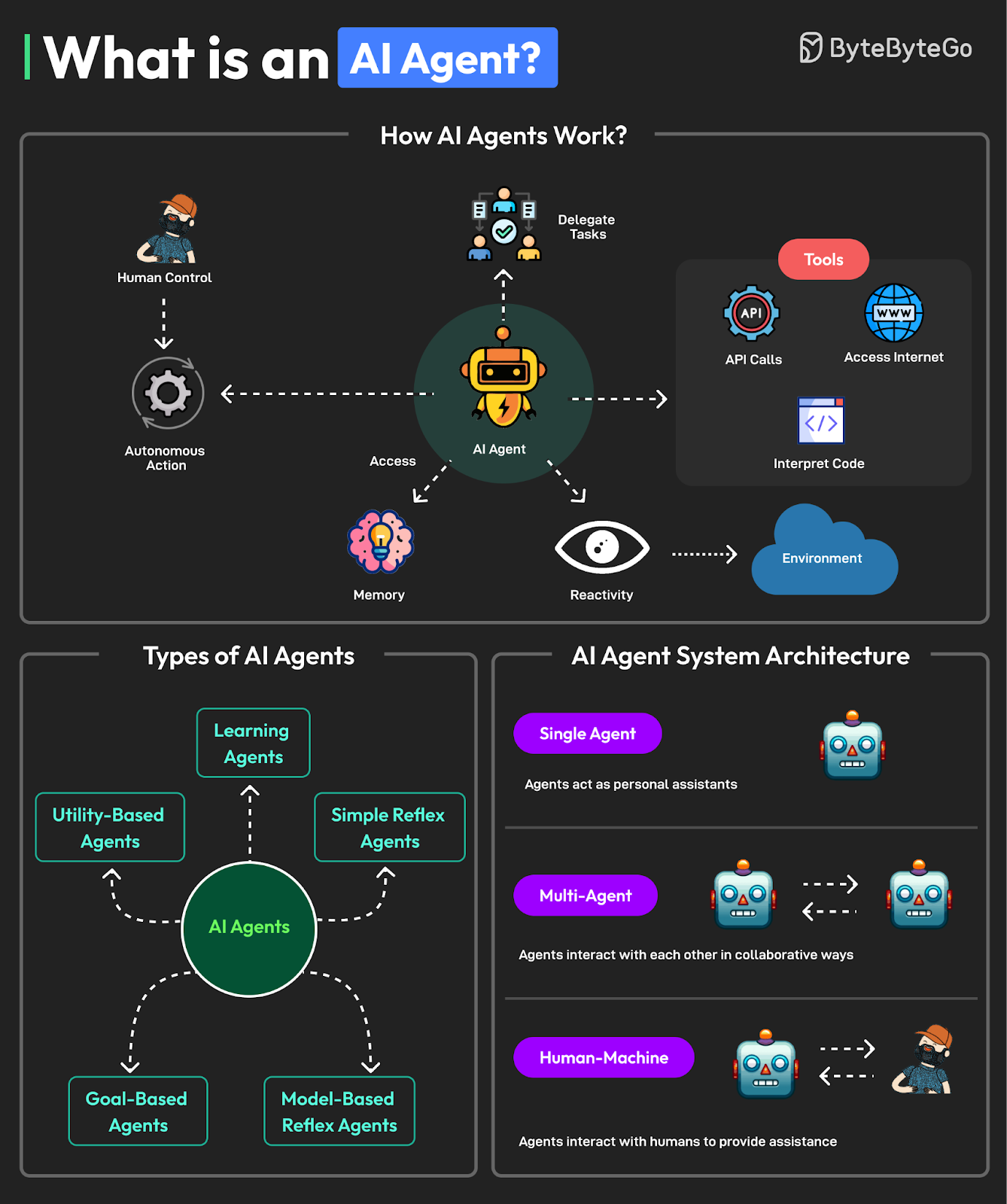
What’s an AI agent?
An AI agent is a system that can make decisions and take actions on its own to achieve a goal. Unlike traditional software that only follows fixed instructions, an AI agent can sense what’s happening around it, think through its options, and choose what to do next — often without human input. In simple terms, it's like a digital assistant that doesn't just wait to be told what to do, but figures out what needs to be done and goes ahead with it.
For example, imagine a travel booking agent powered by AI. You could tell it, “I want to go to Italy in July,” and instead of just giving you links, it checks flight prices, compares hotels, finds you a good deal, and sends you an itinerary — all in one go.
Or think of a smart home assistant that notices you always turn off the lights and lock the door at 10 p.m., and starts doing it automatically for you.
These AI agents aren’t just answering questions — they’re actively helping, based on your goals or habits.
AI agents show up in all kinds of real-world tools: customer service bots that handle support tickets, software that writes reports or creates content, self-driving cars that navigate roads, and even warehouse robots that organize shelves.
What ties them all together is this 👇
AI agents are not just reacting based on pre-defined commands — they’re acting and reasoning, with purpose and goals.
AI Agent vs Automated Workflow: What’s the difference?
Many of the so-called “agents” showcased on social media these days are simply complex automated workflows, like this one ⤵️
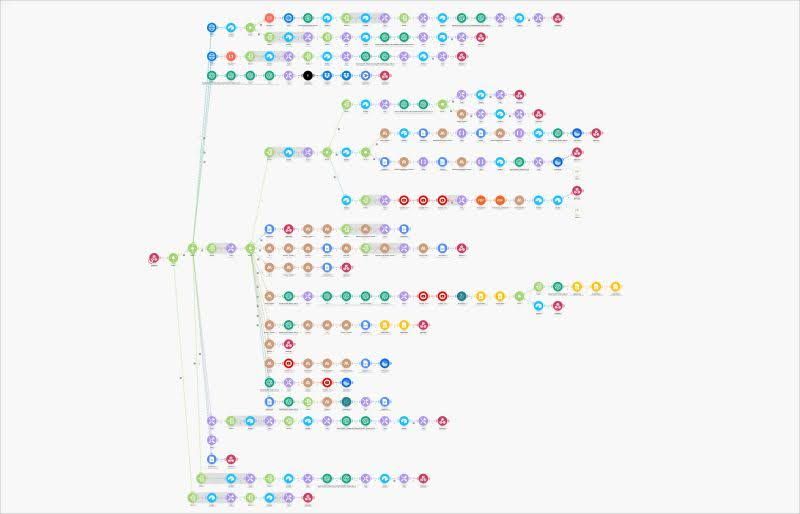
Yes, running this system will “act” as an agent, meaning it will take automated actions and act on it’s own (based off a specific trigger).
However, it does not reason or act on it’s own.
Real AI agents can be simple systems like the one below ⤵️. The difference is that some steps, instead of being a pre-defined action or logic, are calls to AI models.
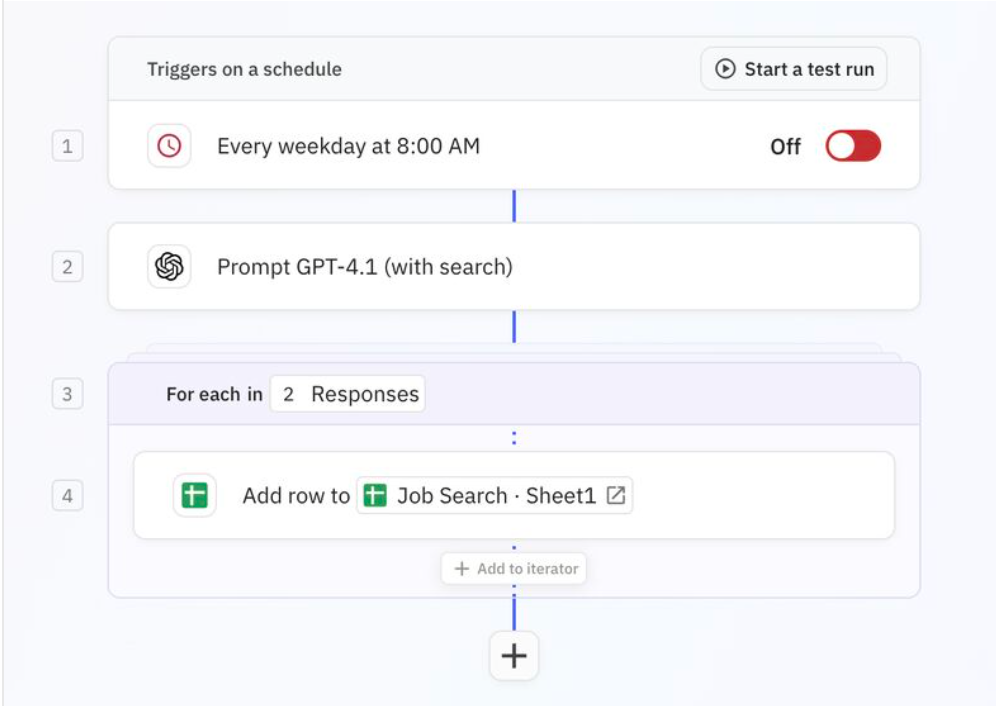
AI agent vs ChatGPT or other AI models: What’s the difference?
🧠 AI Models (like ChatGPT, Claude, Groq) are brilliant minds, but they need someone to ask them questions. They don’t do anything on their own.
They can generate text, understand language, summarize, answer questions, and even write code, but they don’t remember past tasks, use tools, or take action unless a human gives them specific prompts.
🤖 AI Agents
AI Agents use models like ChatGPT as a brain, but add memory, tools, goals, and initiative.They don't just answer — they act.
Think of them like:
An AI agent is a full employee. It uses ChatGPT as its brain, but also checks your calendar, sends emails, books appointments, or tracks down files — all without asking you every step of the way.
Jacob Bank, founder and CEO of the AI agent builder Relay.app, summarized the difference really well in a LinkedIn post.
He aimed to answer: "When should you use ChatGPT vs. an AI agent/workflow tool?"
Here's his explanation ⤵️
1. Use ChatGPT (or another chatbot like Claude or Gemini) if:
- It's a one-off use case that you aren't doing very frequently
- If the input and output is primarily text
- If you want to chat and refine the output
For example, if you want to create an annual marketing strategy, ChatGPT is perfect. You don't do it very often, you want a text report as output based on your text prompt as input and you want to go back and forth and refine the report with the AI.
2. Use an AI agent/workflow tool (like Relay.app, Zapier, Lindy, or Gumloop) if:
- It's a frequently repeated use case
- If it needs to access structured data from your tools
- If it needs to automatically take action in your tools
For example, if you want to create a weekly marketing performance report, this is a perfect fit. You do it every week. You need to pull data from spreadsheets, emails, docs, etc. And you need to put the output automatically in a doc or Slack.
AI agent vs AI chatbot: What’s the difference?
Same with a model, the difference between AI agents and AI chatbots is initiative + action (or lack thereof)
Most AI-powered chatbots will answer questions. Here’s an example 👇
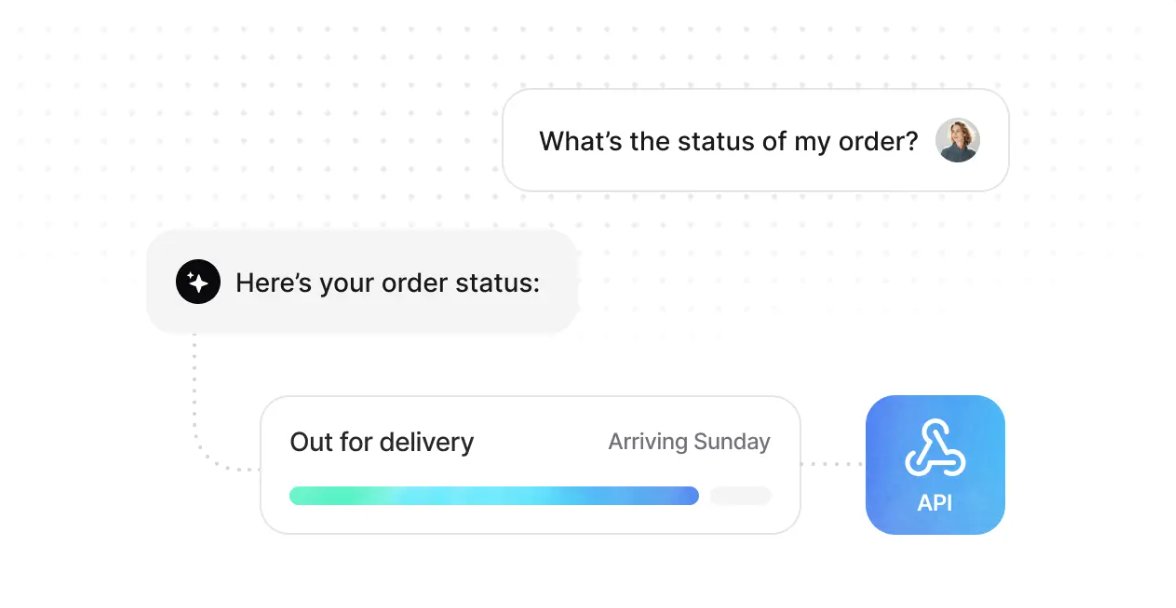
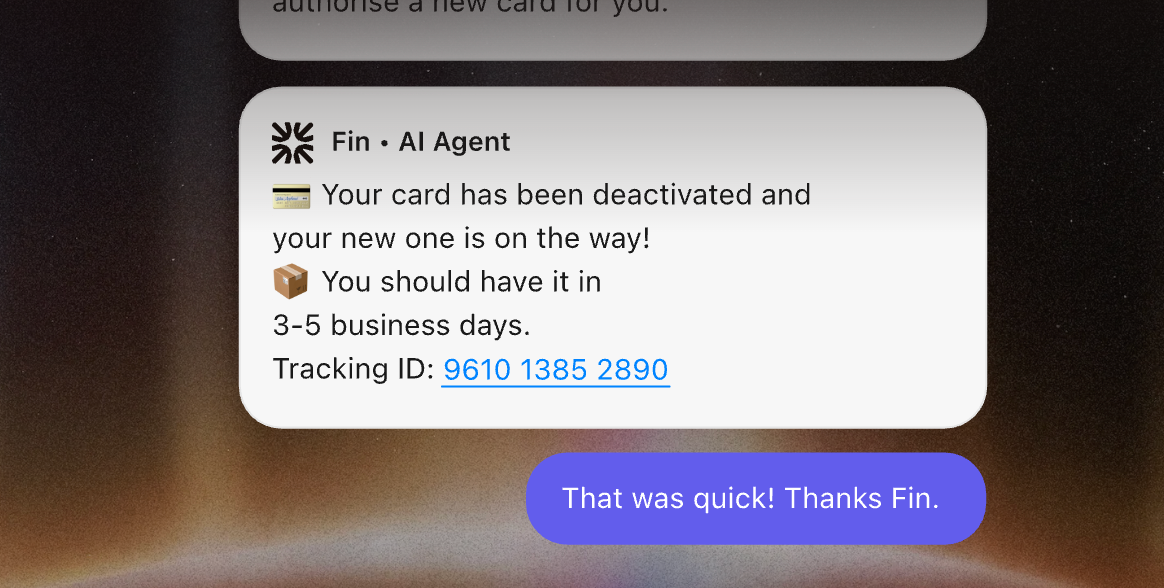
Action agents will solve a problem and take action. Here’s an example 👇
AI agent vs AI-powered software: What’s the difference?
Different types of AI agents
1. Simple Regex Agents
What it is: Basic rule-followers. These agents use pattern matching (like “if you see X, do Y”).
How it works: They rely on regular expressions to recognize specific words or phrases, with no deep understanding or continuous learning.
Real-world example: An AI support agent that can reorder a new credit card when yours is stolen and you’ve verified your identity (Fin AI example above).
2. Model-based
What it is: Smarter agents that build a simple "map" of their environment to make better decisions.
How it works: They keep track of what’s going on — not just reacting blindly — and choose actions based on their model.
Real-world example: a smart thermostat that adjusts your temperature settings based on past behaviour (e.g., you always lower the temperature at 10 p.m.).
3. Goal-based
What it is: Agents that act based on a specific goal they’re trying to reach.
How it works: They ask themselves: “Will this action get me closer to my goal?” — and choose accordingly.
Real-world example: An AI assistant aiming to book a vacation within your budget.
4. Utility-based
What it is: Goal-based agents, but smarter — they don't just want any solution, they want the best one.
How it works: They score each option (“utility”) and choose the one with the highest benefit.
Real-world example: A software database AI agent that dynamically assigns smart storage to optimize performance
5. Learning Agents
What it is: Agents that get better over time by learning from experience.
How it works: They adapt by watching what works and what doesn’t — sometimes with feedback, sometimes on their own.
Real-world example: A robot vacuum that remembers room layouts
6. Reasoning Agents
What it is: Agents that think through problems like a human might — using logic, deduction, and memory.
How it works: They break down complex tasks into smaller steps and make decisions using structured reasoning.
Real-world example: An assistant that builds a to-do list based on your priorities and deadlines in your Google Suite systems (Gmail, Google Calendar, etc.)
7. Robotic Agents
What it is: AI agents that exist in the physical world — they sense, think, and act using hardware.
How it works: They use sensors to understand their surroundings, make decisions, and take action (like moving or picking something up).
Real-world example: A self-driving car.
8. Cluster agents
What it is: Many agents working together — like a team — to solve a problem.
How it works: Each agent has its own role, but they collaborate (or sometimes compete) to reach a shared outcome.
Real-world example: AI agents managing different departments in a company
Examples of what you can do with AI agents
💡 Read more: 15 Real-Life Examples of AI Agents in 2025
6 Free Out-of-the-box AI Agents you can try today
Big Sur AI: Delight your customers and drive more conversions with AI.
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: AI-first chatbot assistant, personalization engine, and website content marketer. Big Sur’s AI agents interact naturally with visitors anywhere on your site, providing relevant, helpful answers that guide users toward their goals — whether that’s making a decision, finding information, or completing an action.
Librarian: Your personal AI assistant
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: WhatsApp AI Assistant designed to help master your inbox, control your schedule, and find anything. It integrates with all your Google Apps (Gmail, Drive, Calendar, Contacts), Notion and Slack.
Canva AI: Your design AI
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: Canva AI is an integrated suite of AI-powered tools within Canva designed to simplify and enhance the creative process for users of all skill levels. It assists in generating, editing, and optimizing content efficiently.
Micro AI: An AI Agent that writes and fixes test-driven code from natural language descriptions.
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: It uses unit tests as guardrails to ensure the generated code meets specified requirements. The tool constrains the AI to specific tasks, generates unit tests based on user prompts, writes code to pass these tests, and automatically iterates until all tests pass.
Garnit AI: Never dig through promo emails again
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: Garnit finds the top deals in your promotional emails, saving you the headache of actually having to read them. It also reminds you when deals you've saved are about to expire.
Lovable: your personal full-stack engineer
Link to website: Click here.
What it does: Lovable lets you turn your idea into a real, working app or website without writing code.
How to Build & Deploy AI Agents
Option 1: Leverage an AI Agent Solution
You can leverage solutions that offer “out-of-the-box” AI agents. These companies have built agent systems to solve specific problems without requiring customers to develop their own.
Pros of leveraging an AI agent solution
✅ Get your agent deployed quickly
✅ Easy to set up without technical knowledge
Cons of leveraging an AI agent solution
❌ Some tools have free plans, but most solutions will incur a cost
Big Sur AI is one of them. Here’s how it works ⤵️
How to Launch Your AI Chatbot With Big Sur AI in Minutes
- Sign up on Big Sur AI's Hub (link here).
- Enter your website URL. Big Sur AI will automatically analyze your site content.
- Customize your AI agent. Set up specific AI actions and decide where the AI agent will appear on your site.
- Launch and monitor. Your AI agent will be live in minutes, and you can track performance with real-time analytics.
Option 2: Build it yourself
The other option is to use agent builder platforms to customize your own AI agent. This option requires more work upfront, but adds more flexibility. Some platforms are general AI agent builders, and others are specific to an industry or function (more on this below).
Pros of building an AI agent yourself
✅ More customization & flexibility
✅ Can be cheaper (although agent-building platforms have costs too)
Cons of leveraging an AI agent solution
❌ Time-consumine (building + maintaining)
❌ Requires technical expertise
General AI Agent Tools
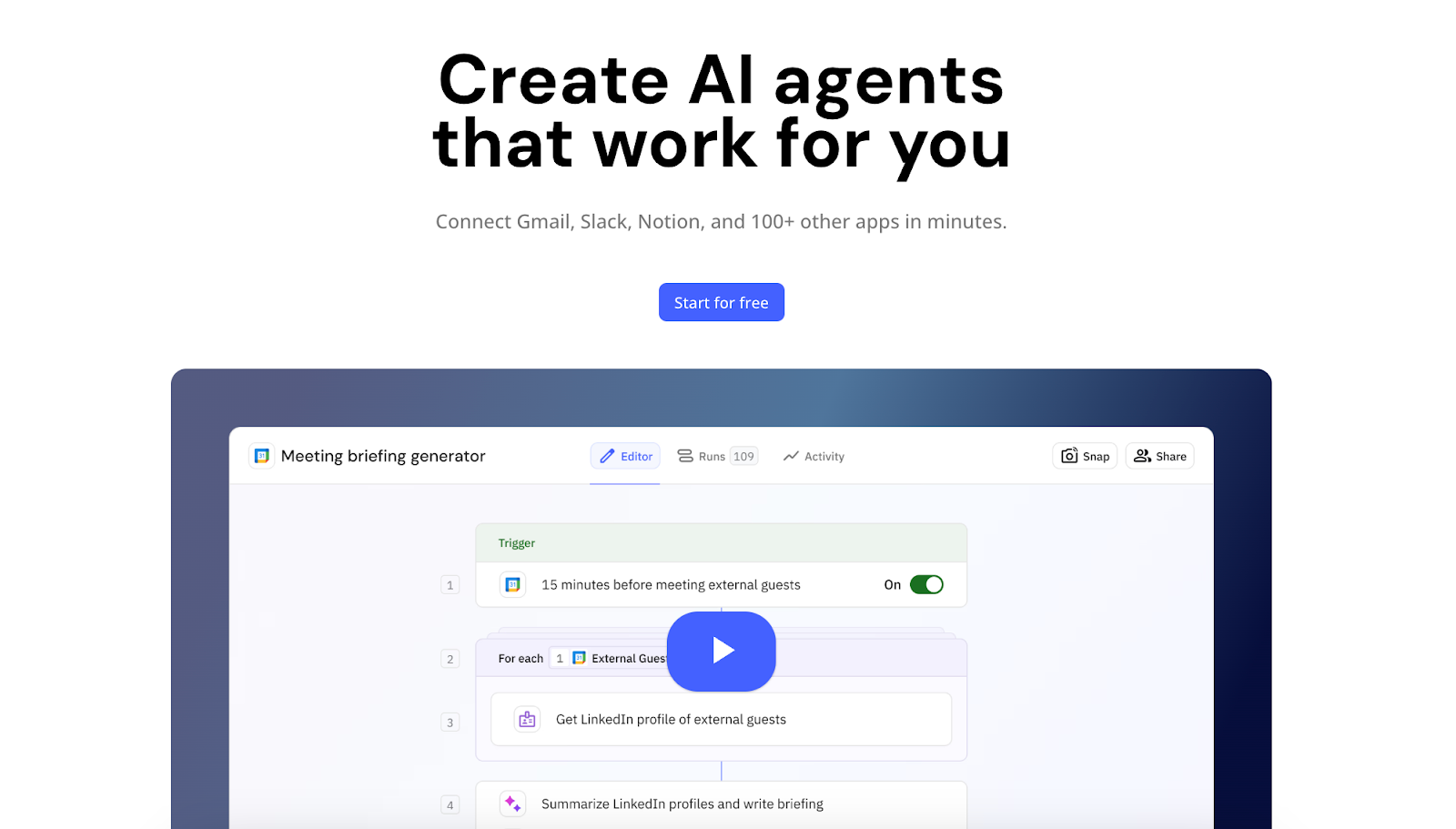
Use case: Build any AI agent, AI-powered workflow, or AI cluster system.
Popular apps: Relay.app, Zapier, Botpress, n8n, Make.
Function or Industry-Specific AI Agent Solutions
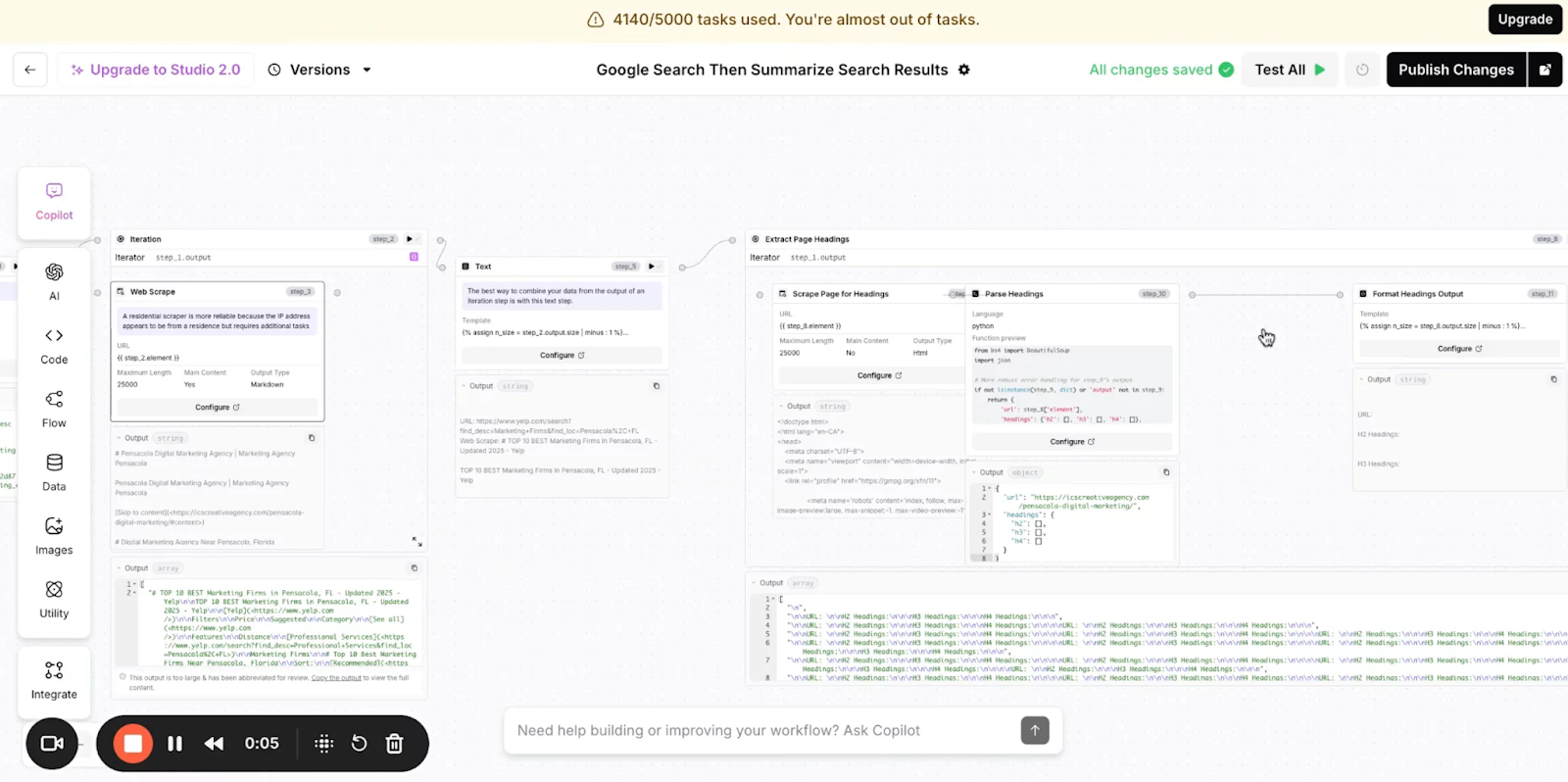
Use case: Build an AI agent for a specific function or use case like content production (AirOps), or sales prospecting (Clay).
Popular Apps: AirOps, Clay, Warmly, Fin AI (Intercom), and more.
Ready to Launch your Website’s AI Chatbot Agent?
Try Big Sur AI on your site in minutes by clicking the image below 👇


